What is Natura 2000?
Natura 2000 is an ecological network composed of areas important for the conservation of endangered species and habitat types of the European Union. Its goal is to preserve or restore the favorable status of more than a thousand endangered and rare species and about 230 natural and semi-natural habitat types. So far, about 27,500 areas in almost 20% of the EU's territory have been included in this ecological network, making it the largest system of preserved areas in the world. Natura 2000 is based on EU directives, areas are selected by scientific criteria, and the management of these areas takes into account the interest and well-being of the people living in them.
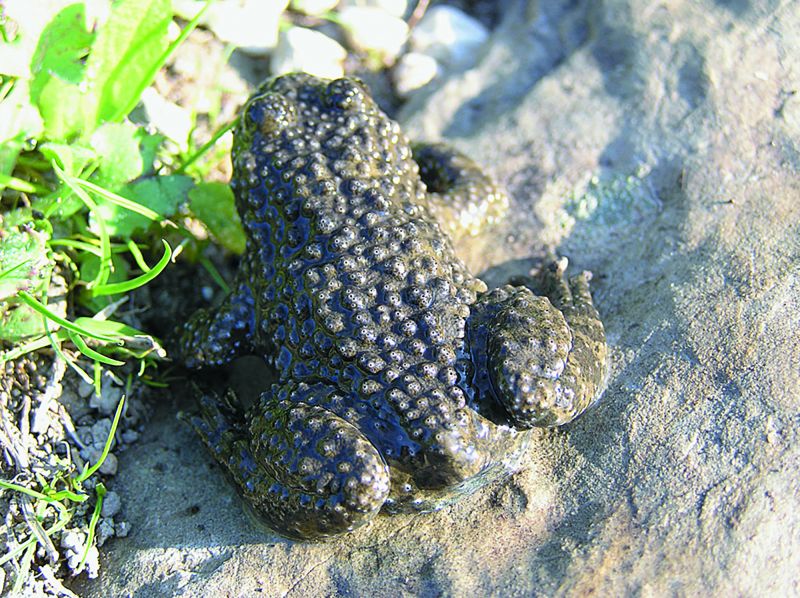
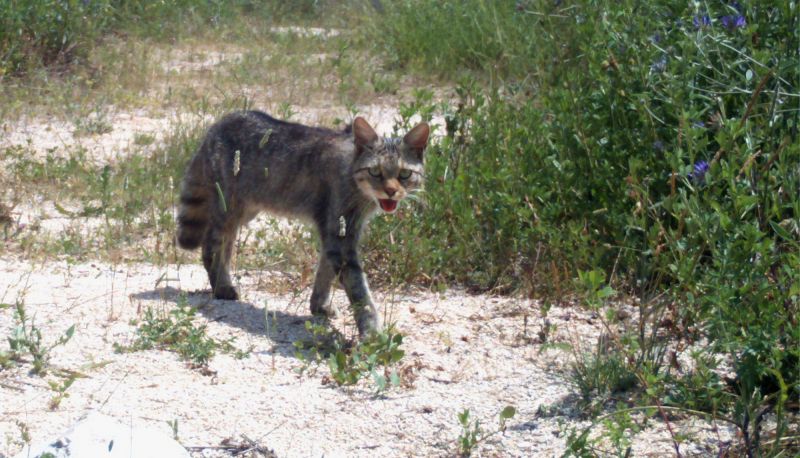
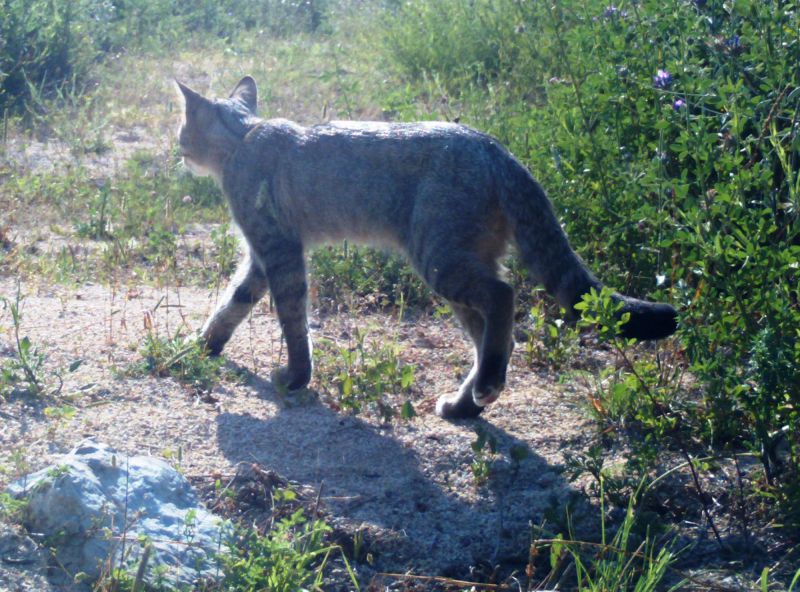
Although largely altered by human activity, European nature includes a very large diversity of habitats. Extensive natural forests, meadows and pastures, wetlands and unregulated rivers, marine, subterranean and other habitats inhabited by numerous species still represent the rich natural heritage of Europe. Many of these habitats are the result of traditional land use, which does not endanger but enriches biodiversity. Over the last decades, human activities and the use of natural resources have changed significantly around the world. The state of biodiversity has deteriorated dramatically in the last 50 years, more than in the entire history of mankind. Due to human activities, species become extinct 1000 times faster than under natural circumstances. These losses overshadowed the productivity of nature and thus endangered the long-term survival of mankind. More than 700 species, mostly birds and mammals, are listed in the Red List of Endangered Species in Europe. Not only rare or endemic species are endangered, but also many species that are still numerous, but their suitable habitats are rapidly disappearing, which can lead to their imminent extinction. Natura 2000 is a fundamental program by which the European Union tries to stop these negative trends on its territory.
 English
English










 Parks of Croatia
Parks of Croatia